Packet Analysis
Meaning:
Packet analysis is a technique used to capture and intercept network traffic that passes the computers network interfaces. May also be called different names like packet sniffer, packet analyzer, protocol analyzer or network analyzer.
Tools:
Wireshark is one of the tools most of used to intercept network traffic, it has five major components.
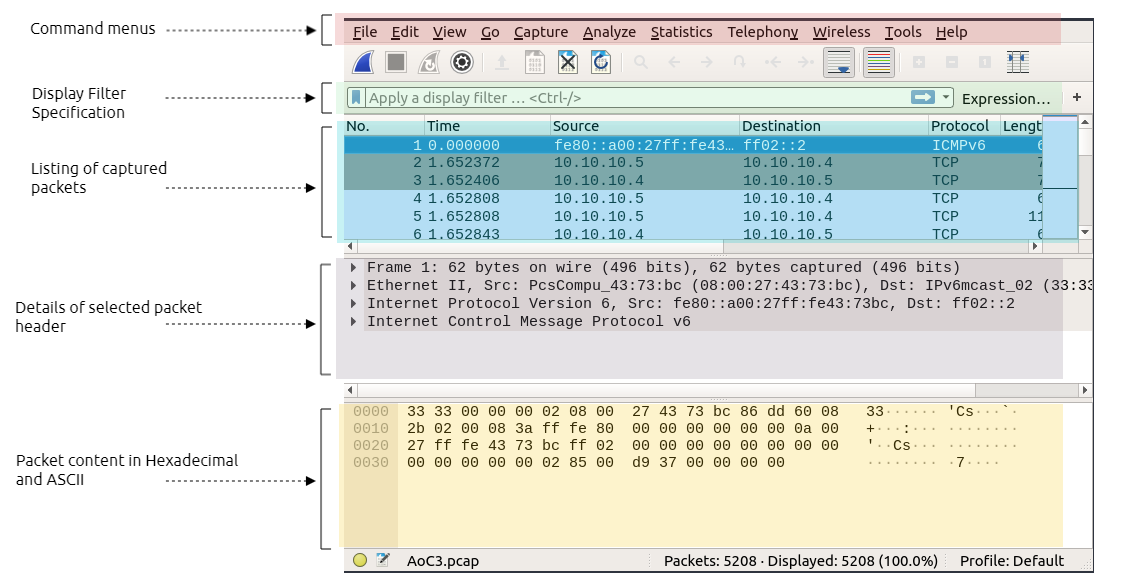
- Command menus are standard pull down menus located at the top of the window. The File menu allows you to save captured packet data or open a file containing previously captured packet data, and exit the Wireshark application
- Display filter section is where we can specify rules to find certain packets. The listing of captured packets shows all sent and received network packets. This section includes important fields that are used in the filter section, such as
source and destination IP addresses,protocols, andinformation - Details of a selected packet header section shows details about selected network packets and shows all headers, including all
TCPlayers information - Packet content section which shows the packet content in
hexadecimalandASCIIformat
Wireshark Filters:
Barley Packet Filter (BPF) syntax is used in packet analyzers to filter specific packets pre-capture. Filtering packets is beneficial when locating information withing a packet capture process (PCAP)
| COMMAND | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
ip.addr == 172.21.2.116 | Looking for all packets that have been sent or received by the given IP address |
http | Showing all packets that were sent with a specific protocol |
http contains google.com | Showing all packets that were sent with a specific protocol to a specific domain |
tcp.port = 3389 | Showing all packets that were sent with a specific port |
not tcp.port = 3389 | Filters out all the given items that were sent with a specific port |
http.request.metod == GET | Showing all HTTP protocol packets with the given request |
udp.port == 53 or dns | Showing all packets that were sent with DNS (alternatively tcp.port == 53 might work too, per default tough DNS used UDP) |
tcp.port == 21 or ftp | Showing all packets that were sent with FTP |
ftp-data | Showing all file packets uploaded with FTP |
GET
Inspecting GET (double-clicking the given GET request) allows us to see additional information about the sender request such as the IP address of the host, web user agent and other information.
POST
Inspecting POST (right click –> follow –> TCP Stream), allows us to see the web request and their details like the Cookie, username, password, HTML page and other information.
DNS
DNS is like a giant phone book that takes a URL and turns in into a IP address. This means people don’t have to remember IP addresses for their websites and can instead use the domain address.
Inspecting DNS (double-clicking the given DNS request) allows us to see additional information in the Domain Name System (query). Showing whether the query is a Question, Answer RRs, Authority RRS or Additional RRS. Additionally, we can see which type of record the user is asking for (A etc.) and before that the domain name we are trying to access (packet.tryhackme.com).
Moreover, each Question has an Answer meaning the server we request gives back a IP address, to find that Answer we can use the Transaction ID and search for it via
response <Transaction ID> <type> <domain name> --> response 0xef8e A packet.tryhackme.com
Then by double-clicking on the required packet, we can see that it has an answer section which shows the IP address to the domain name.
We can also inspect DNS if we right-click –> follow –> UDP Stream
FTP
Inspecting FTP (right-click –> follow –> TCP Stream), to see files uploaded by a logged-in user. We will not see the packet of the actual uploaded file for that we need to use ftp-data filter to list the packets that have the content of the file.