No SQL
Meaning:
A NoSQL database refers to a non-relational database that is short for non SQL and Not only SQL.
Example:
There are a variety of NoSQL databases, including MongoDB, Couchbase, RavenDB, etc.
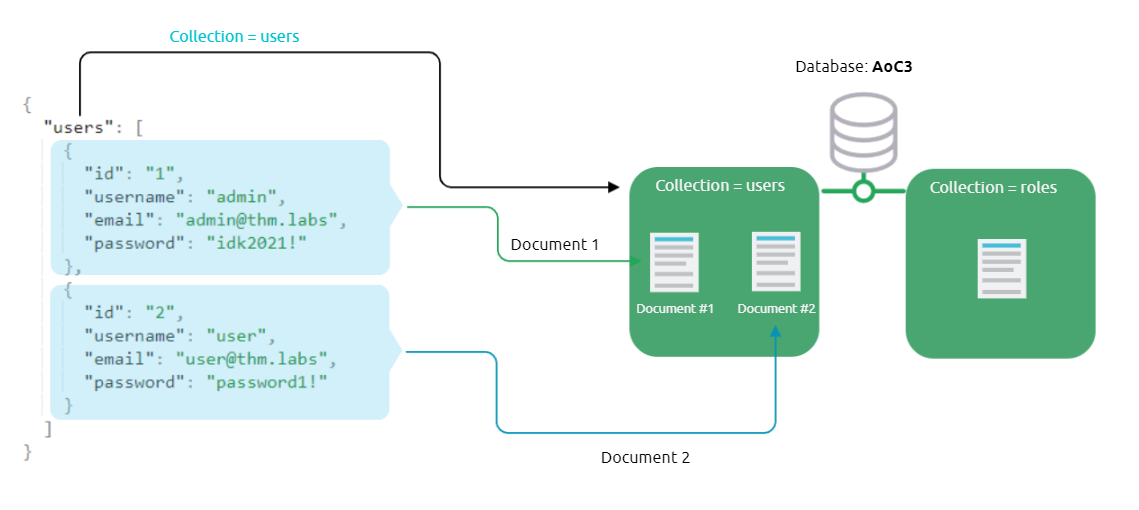
Mongo DB structure:
Similar to relational databases (such as MySQL and MSSQL), MongoDB consists of databases, tables, fields but with different names where:
- Collections are similar to tables or views in
MySQLandMSSQL - Documents are similar to rows or records in
MySQLandMSSQL - Fields are similar to columns in
MySQLandMSSQL
Documents in MongoDB are objects stored in a format called BSON, which supports JSON data types for document storing.
Query operators between MongoDB and MySQL:
$andequivalent toANDin MySQL$orequivalent toORin MySQL$eqequivalent to=in MySQL
MongoDB commands:
| COMMAND | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
ssh thm@10.10.80.25 -p 2222 | Connecting to the server via. ssh |
mongo | Starting MongoDB |
show databases | Listing all databases that we have in MongoDB on our target machine |
use AoC3 | Connecting or creating a database that hasn’t been created yet |
db.createCollection("users") | Creating Collection with a given name |
db.getCollectionNames() | Getting all collection names in the given database |
db.user.inser({id:"1", username:"admin", email:"admin@thm.labs", password:"idk2021!"}) | Creating a Document with a given Collection and insert data into it |
db.users.find() | Get all Documents in a given Collection |
db.users.update({id:"1"}, {$set: {username: "tryhackme"}}) | Update a value of a Document in a given Collection |
db.users.remove({id:"2"}) | Remove Document from a given Collection |
db.users.drop() | Destroy Collection |
db.users.findOne({username: "admin", password: "adminpass"}) | Gets one Document in a given Collection with the given query data. If nothing is found null is returned |
NoSQL Injection:
NoSQL injection is a web security vulnerability that allows the attacker to have control over the database. It happens by sending queries via untrusted and unfiltered web application input, which leads to leaked unauthorized information. In addition, the attacker can use the NoSQL injection to perform various operations such as modifying data, escalating privileges, DoS attacks, and others.
MongoDB Operators:
$eqmatches records that equal to a certain value$nematches records that are not equal to a certain value$gtmatches records that are greater than a certain value$wherematches records based on a JavaScript condition$existsmatches records that have a certain field$existsmatches records that satisfy certain regular expressions
Example NoSQL Injection:
Searches for a Document where the username is admin and the password is not xyz.
db.users.findOne({username: "admin", password: {"$ne":"xyz"}})
Exploiting NoSQL Injection with GET or POST:
Injecting [$ne] int the password parameter.
?username=admin&password[$ne]=xyz