Nmap
Meaning:
Nmap is a network scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing responses.
IP address:
Every computer (host) that connects to a network needs to have a logical address. We refer to this address as logical because it’s assigned by software and could change over time, for example, when the host connects to a new network. The logical address, in this case, is the IP address.
IP stands for Internet Protocol. For example a IPv4 address is made up of 4 decimal numbers, they each range from 0 to 255.
Example IPv4 addresses:
- 192.168.0.10
- 172.16.0.100
- 10.10.11.12
- 1.1.1.1
The first 3 IP addresses in the list above are private, meaning they can only be accessed from the private network they belong to. The last IP address however is a public IP address that can be accessed by the whole internet and belongs to Cloudflare.
Some IP addresses serve a special purpose for example 127.0.0.1, which is often referred to as the loop back address or localhost. By default, any packet or traffic destined to this address won’t leave the host.
Finding your IP address:
Windows: ipconfig Linux and macOS: ip address show / ip addr show / ip a s
Protocols and Servers
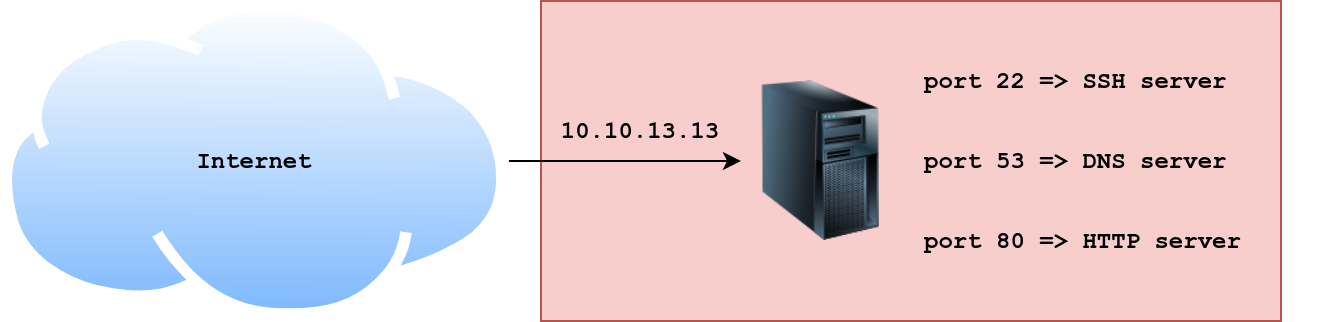
If we want to set up a website that we’ve made accessible to the whole Internet. In order to make our website accessible to the users, a public IP address is required. A web server is a program that listens for incoming connections, usually from web browsers, and responds to their requests.
A server usually refers to a computer system that provides services to other clients, over a network. For example serving webpages, delivering email and facilitating video conferencing.
For the client computer to communicate with the server, a specific protocol must be followed. Here is an example with ordering an espresso from a coffee shop to visualize how that would work.

TCP/IP protocols:
Hypertext Transfer Protocol(HTTP) for serving webpagesDomain Name System(DNS) for resolving hostnames to IP addressesPost Office Protocol version 3(POP3) for delivering emailSimple Mail Transfer Protocol(SMTP) for sending emailTelnetfor remote loginSecure Shell(SSH) for secure remote login
Ports
On a host multiple processes (programs) can be accessing the network at the same time. These processes can use the network simultaneously. For the host to tell which process receives which packet, we need to use port numbers.
Common protocols and their respective default port numbers.
| PROTOCOL | PORT NUMBER |
|---|---|
HTTP | 80 |
HTTPS | 443 |
POP3 | 110 |
SMTP | 25 |
SSH | 22 |
Telnet | 23 |
TCP and UDP live on top of the IP protocol and connect process running on different hosts. More importantly TCP requires a three-way handshake for a connection, while UDP does not. Therefore, UDP is faster but TCP ensures our packets are sent / received.
Using Nmap
We can run a very basic network port scan using the commands.
nmap -sT 10.10.173.86, to scan each port with a three-way handshake
nmap -sS 10.10.173.86, to scan each port without a three-way handshake
nmap -sV 10.10.173.86, to scan each port and detect the web server version number
By default, Nmap checks the 1000 most common TCP ports. Adding -p1-65535 or -p- tough will increase that amount to scan all 65’535 TCP ports.
There is also an additional setting -Pn for system that do not respond to ping probes, to ensure Nmap skips pinging the target to see if the host is reachable, without this Nmap will assume the target host is offline and will not continue with scanning.
TCP Connect Scan: To run this type of scan, the -sT option is required. Nmap will attempt to complete the three-way handshake in order to establish a connection with each port scanned. TCP SYN Scan: You can select this scan with the -sS option, and Nmap will not make a complete connection if the port is open. Technically speaking, Nmap does not complete a TCP three-way handshake.
To better understand the difference between -sT and -sS, we can use the analogy of knocking on a door. The TCP connect scan (-sT) is like knocking on a door, waiting for someone to open it, greeting each other, then excusing yourself to leave. The TCP SYN scan (-sS) resembles knocking, and once someone answers, you pretend that it was not you that knocked and walk away innocently. The latter will make it more difficult for the other party to remember you.