Networking
Meaning:
Networks are simply things that are connected. They can be found in all walks of like:
- A city’s public transportation system
- Infrastructure such as the national power grid for electricity
- Meeting and greeting your neighbors
- Postal system for sending letters and parcels
In computing, however, networking is the same idea, just dispersed to technological devices and can mean anything from connecting 2 devices to up to billions of devices.
Internet:
The internet is one giant network that consists of may, many small networks within itself.
The first iteration of the internet was within the ARPANET project in the late 1960s. It was funded by the United States Defense Department and was the first documented network in action.
However, it wasn’t until 1989 when the internet as we know it was invented by Tim Berners-Lee by the creation of the World Wide Web (WWW).
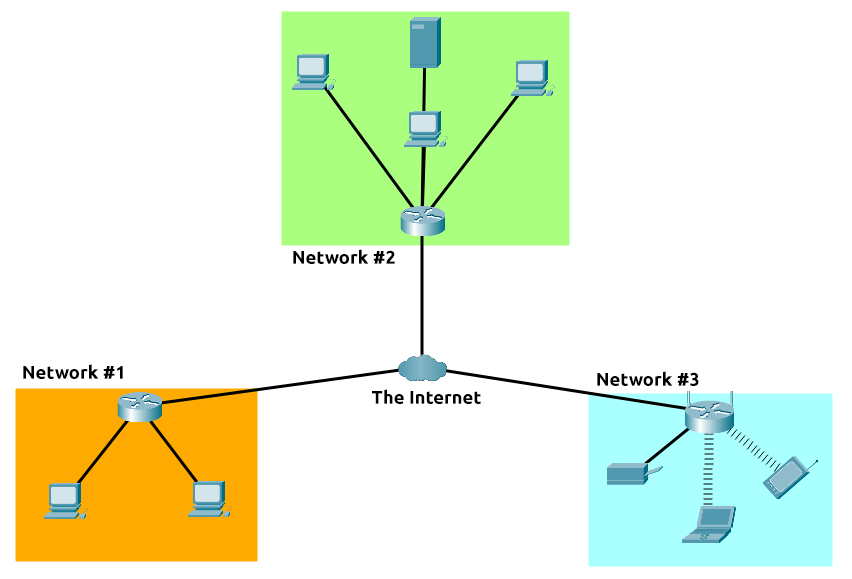
The internet is made up of many small networks all joined together. These small networks are called private networks, where network connecting these small networks are called public networks, or the internet.
So networks can be one of these two types:
- Private network
- Public network
Devices additionally use a set of labels to identify themselves on a network.
Identifying Devices:
To communicate and maintain order, devices must be both identifying and identifiable on a network. There are two ways to ensure devices on a network are identified:
IPAddress, similar to a name can be changed- Media Access Control (MAC) Address, similar to a fingerprint or serial number and cannot be changed
IP Address:
Can be used as a way of identifying a host on a network for a period of time, where that IP address can then be associated with another device without the IP address changing.
It consists of a set of numbers that are divided into four octets, where each octet consists of a number from 0 to 255. The address can change from device to device but cannot be active simultaneously more than once within the same network.

As recalled earlier devices can be on both a private and public network. Depending on where they are will determine what type of IP address they have, which is also either public or private.
| DEVICE NAME | IP ADDRESS | IP ADDRESS TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| DESKTOP-KJE57FD | 192.168.1.77 | Private |
| DESKTOP-KJE57FD | 86.157.52.21 | Public |
| CMNatic-PC | 192.168.1.74 | Private |
| CMNatic-PC | 86.157.52.21 | Public |
In this case both devices will be able to use their private IP address to communicate with each other. However, any data sent to the internet from either device will be identified by the same public IP address, which is provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
IPv4 which we discussed above uses a numbering system of 2^32 IP address (4.29 billion). Sadly this is not enough anymore which is the reason a new iteration of Internet Protocol addressing scheme called IPv6 was created. It supports up to 2^128 IP address (340 trillion) and is even more efficient due to new methodologies.
IPv6: 2a00:22c4:a531:c500:425f:cce6:c36b:f64d IPv4: 86.157.52.51
MAC Address:
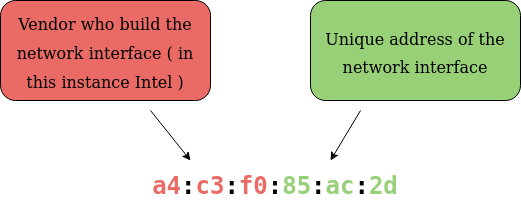
Devices on a network all have a physical network interface, which is a microchip board found on the devices’ motherboard. This network interface is assigned a unique address at the factory it was built at, called a MAC (Media Access Control) address.
It is a twelve-character hexadecimal number split into pairs of two and separated by a colon. The first six characters represent the company that made the network interface, and the last six are a unique number.
Spoofing:
A MAC address can be faked in a process know as spoofing. It occurs when a networked device pretends to identify as another using its MAC address. When this occurs, system that assume that devices talking on a network are trustworthy can often break.
Often places such as cafés, coffee shops, and hotels alike often use MAC address control when using their "Guest" or "Public" Wi-Fi.
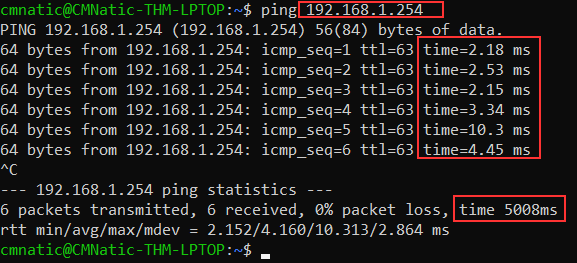
Ping (ICMP):
Ping uses ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets to determine the performance of a connection between devices. For example if the connection exists or is reliable.
The time taken for ICMP packets travelling between devices is measured by ping. This is done using the ICMP echo packet and then the ICMP echo reply from the target device.
Pings can be performed against devices on a network. The syntax to do a simple ping is ping IP address or website URL.